CRYSVITA: Efficacy results in adults with XLH
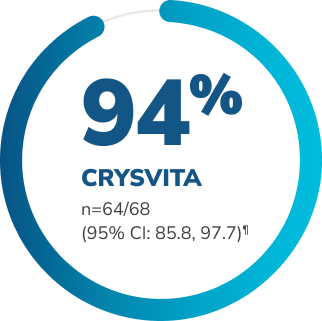
Significantly more patients receiving CRYSVITA achieved mean serum phosphorus levels above the LLN† through 24 weeks vs. placebo1,2‡§
Proportion of patients who achieved mean serum phosphorus levels above the LLN (measured at the midpoint of the dose interval) during 24 weeks of treatment1,2
VS.
p<0.0001††
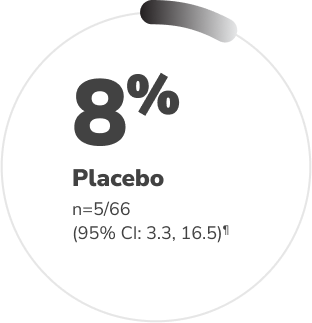
Adapted from the Product Monograph and Insogna KL, et al., 2018.1,2
In patients receiving CRYSVITA, mean serum phosphorus concentrations remained at or above the LLN† through 48 weeks1,3§
Change in serum phosphorus at the midpoint of the dose interval through Week 481,3‡‡
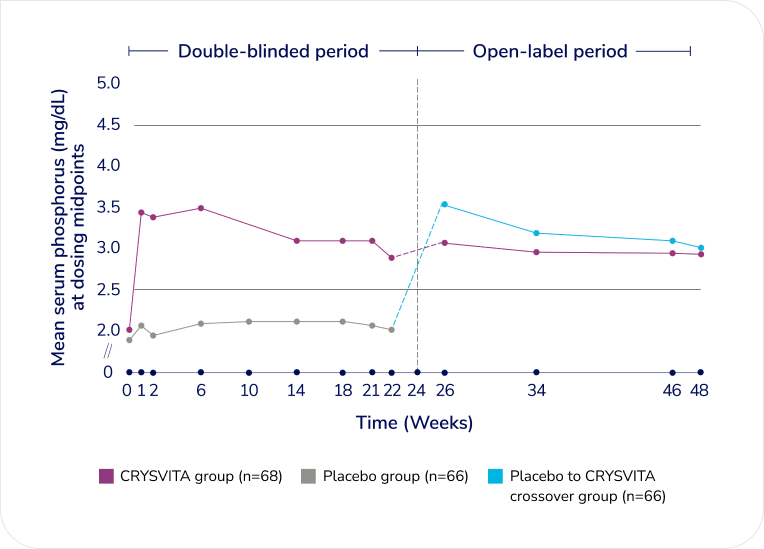
Adapted from the Product Monograph and Portale AA, et al., 2019.1,3
The placebo group was crossed over to CRYSVITA at Week 24.
Note that 1 mg/dL is equivalent to 0.323 mmol/L.4
Mean serum phosphorus concentrations continued to remain above the LLN† through 48 weeks in the initial CRYSVITA treatment group and remained at or above LLN† in the placebo to CRYSVITA crossover group starting from Week 26 through Week 48.1,3
CRYSVITA demonstrated significantly greater improvements in XLH-associated stiffness vs. placebo at Week 24 (secondary endpoint; as measured by the WOMAC Index)1,2§
WOMAC stiffness—LS mean change from baseline to Week 241
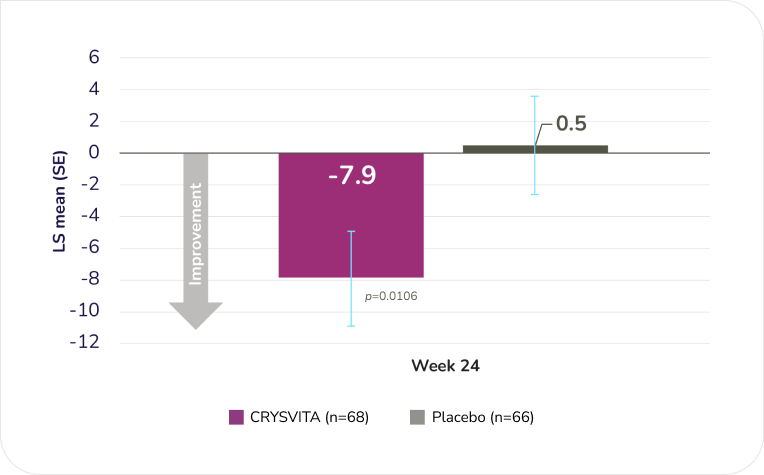
Adapted from the Product Monograph.1
Mean WOMAC stiffness score (SD) declined from 64.7 (20.25) to 53.7 (20.76) in the CRYSVITA group vs. 61.4 (20.77) to 60.4 (21.83) in the placebo group from baseline to Week 24 (LS mean [SE]: CRYSVITA -7.9 [3.03] vs. placebo 0.5 [3.14], p=0.0106).1
The scores on each domain of the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) are normalized and range from 0 to 100 with a higher score indicating poorer functioning.1
Comparison of fracture healing with CRYSVITA vs. placebo (exploratory endpoint)1-3§
| Active fractures | Active pseudofractures | Total fractures | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRYSVITA | Placebo | CRYSVITA | Placebo | CRYSVITA | Placebo | |
| % of fractures healed at Week 24§§ (no. healed/no. at baseline) | 50.0% (7/14) |
0% (0/13) |
41.2% (21/51) |
9.0% (7/78) |
43.1% (28/65) |
7.7% (7/91) |
| % of fractures healed at Week 24§§ (no. healed/no. at baseline) | |
| Active fractures | |
| CRYSVITA | 50.0% (7/14) |
| Placebo | 0% (0/13) |
| Active pseudofractures | |
| CRYSVITA | 41.2% (21/51) |
| Placebo | 9.0% (7/78) |
| Total fractures | |
| CRYSVITA | 43.1% (28/65) |
| Placebo | 7.7% (7/91) |
Adapted from the Product Monograph.1
In the open-label period when all patients received CRYSVITA:1
Patients who continued receiving CRYSVITA: showed additional healing in all three categories.
Patients who started receiving CRYSVITA: showed a higher rate of complete healing in all three categories compared to when they received the placebo.
Osteomalacia-related fractures are defined as atraumatic lucencies extending across both bone cortices, and pseudofractures are defined as atraumatic lucencies extending across one cortex.1
The active fractures/pseudofractures were predominantly located in the femurs, tibia/fibula, and metatarsals of the feet.1
Assessment of the effects of CRYSVITA on the improvement of osteomalacia (as determined by histologic and histomorphometric evaluation of iliac crest biopsies in an open-label single-arm study)1¶¶
After 48 weeks of treatment with CRYSVITA, histomorphometric improvement in osteomalacia was observed in ten patients as demonstrated by decreases in proxy measures.
Osteoid volume/bone volume (OV/BV), n=11
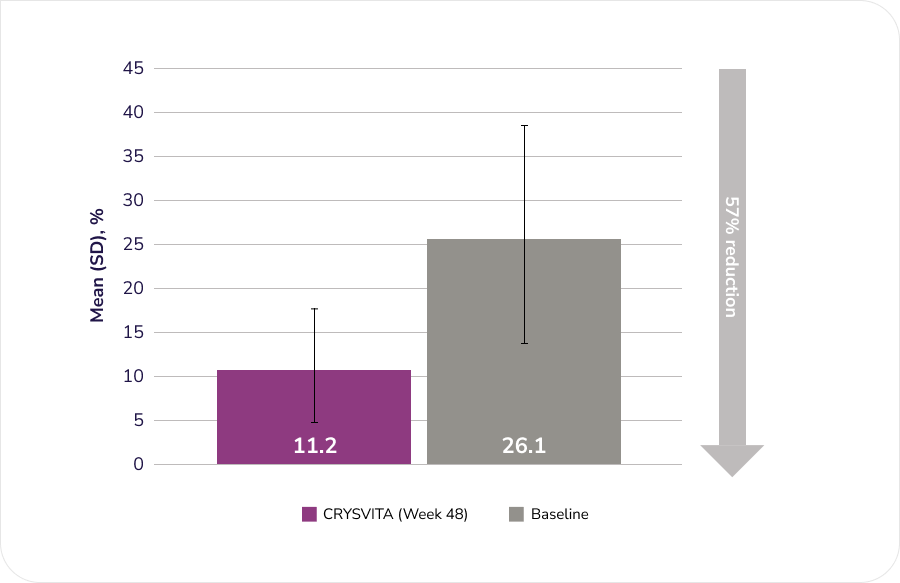
Adapted from the Product Monograph.1
Osteoid thickness (O.Th), n=11
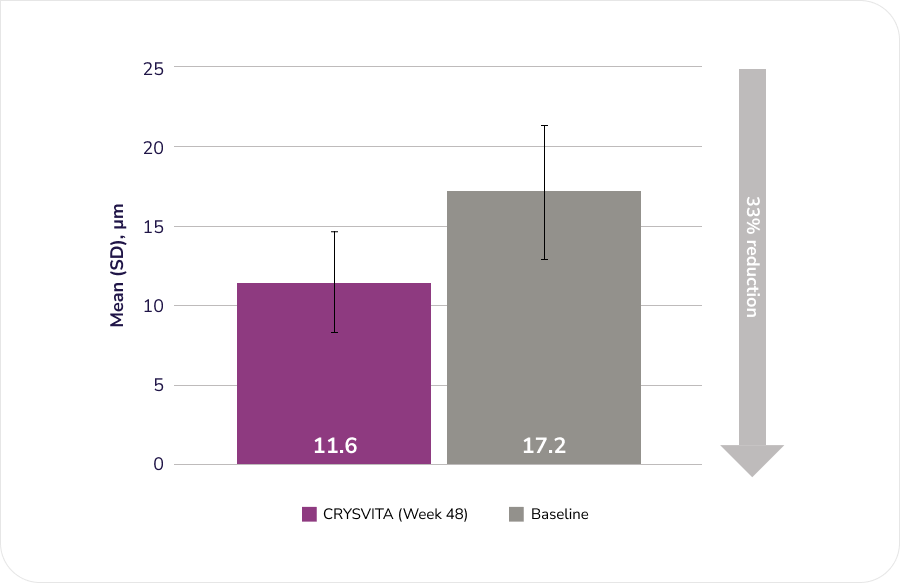
Adapted from the Product Monograph.1
Mineralization lag time (MLt), n=6
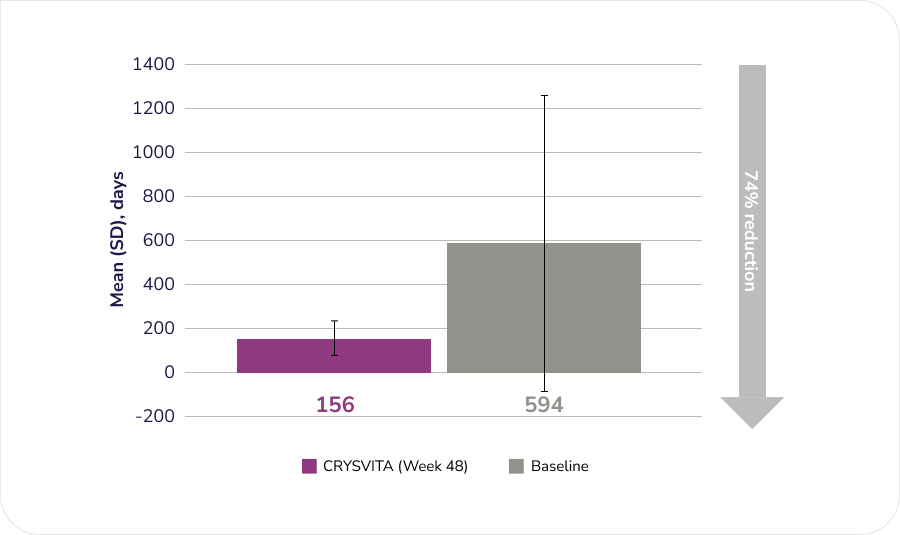
Adapted from the Product Monograph.1
CI=confidence interval; LLN=lower limit of normal; LS=least squares; SE=standard error; SD=standard deviation; WOMAC=Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index.
† The normal range for serum phosphorus used was 2.5–4.5 mg/dL (LLN=2.5 mg/dL), with a dose-limiting toxicity threshold of >6.5 mg/dL.1
‡ Serum phosphorus levels were averaged across the midpoints of the dose interval during 24 weeks of treatment.1,2
§ Phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study in 134 adults with XLH followed by an open-label extension study. Patients were randomized to receive either subcutaneous burosumab 1 mg/kg (CRYSVITA) every 4 weeks (n=68) or matching subcutaneous placebo every 4 weeks (n=66) followed by a 24-week open-label period in which patients randomized to placebo switched to CRYSVITA; all patients remained blinded to their original treatment assignment. Oral phosphate and active vitamin D analogues were not allowed during the study. The primary efficacy endpoint was the proportion of patients achieving mean serum phosphorus concentrations above 2.5 mg/dL (LLN) averaged across the midpoints of the dose interval between baseline and Week 24.1,2
¶ The 95% CIs are calculated using the Wilson score method.
†† P value is from Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel (CMH) testing for association between achieving the primary endpoint and treatment group, adjusting for randomization stratifications.1
‡‡ 1–2 weeks after a dose.3
§§ Percent based on baseline values.
¶¶ Phase 3, open-label, single-arm study in 14 adults with XLH over 48 weeks. The study assessed the effects of CRYSVITA on improvement of osteomalacia as determined by histologic and histomorphometric evaluation of iliac crest bone biopsies. Patients received 1 mg/kg CRYSVITA every four weeks. Oral phosphate and active vitamin D analogues were not allowed during the study. Of the 14 enrolled patients, 11 underwent paired bone biopsies. Mineralization lag time data are only presented for 6 patients; as imputation was required to calculate results for 5 patients due to profound mineralization defects.1,5
References: 1. CRYSVITA (burosumab injection) Product Monograph. Kyowa Kirin Inc. August 13, 2025. 2. Insogna KL, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial evaluating the efficacy of burosumab, an anti-FGF23 antibody, in adults with X-linked hypophosphataemia: Week 24 primary analysis. J Bone Miner Res. 2018;33:1381–1382. 3. Portale AA, et al. Continued beneficial effects of burosumab in adults with X‑linked hypophosphataemia: Results from a 24‑week treatment continuation period after a 24‑week double‑blind placebo‑controlled period. Calc Tiss Int. 2019;105:271–284. 4. ENDMEMO. Available from: http://www.endmemo.com/medical/unitconvert/Phosphorus.php. Consulted October 3, 2023. 5. Insogna KL, et al. Burosumab improved histomorphometric measures of osteomalacia in adults with X-Linked hypophosphatemia: A phase 3, single-arm, international trial. J Bone Miner Res. 2019;34(12):2183-2191.


